Why Smart Contracts Are the Future of Legal Agreements
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, smart contracts have emerged as a revolutionary technology, transforming how agreements are made and executed. These self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code have the potential to automate and secure transactions across various industries. This article explores what smart contracts are, how they work, and their real-world applications, highlighting their impact on modern agreements.
What are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are digital agreements that automatically enforce and execute the terms of a contract when predefined conditions are met. They operate on blockchain technology, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability. Unlike traditional contracts that require intermediaries, such as lawyers or notaries, smart contracts eliminate the need for third-party involvement, thereby reducing costs and potential delays.
A smart contract is essentially a program stored on a blockchain that runs when certain conditions are met. These conditions are coded into the contract, and once triggered, the contract executes itself. The idea was first proposed by computer scientist and cryptographer Nick Szabo in the 1990s, but it gained significant traction with the advent of blockchain technology.
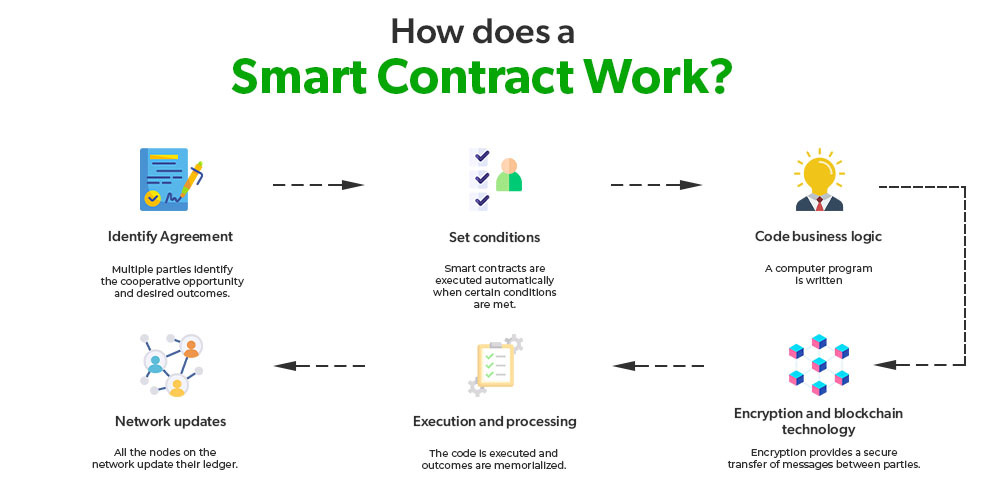
How Smart Contracts Work
Smart contracts function through a straightforward yet powerful mechanism. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how they work:
- Coding the Contract: The terms and conditions of the agreement are written into a smart contract code. This code includes rules and penalties, much like a traditional contract, but it is written in a programming language such as Solidity (for Ethereum-based contracts).
- Deployment on Blockchain: Once the contract is coded, it is deployed onto a blockchain network. Ethereum is the most widely used platform for smart contracts, but other blockchains like Binance Smart Chain, Solana, and Polkadot also support them.
- Triggering Conditions: The contract remains dormant until the predefined conditions are met. These conditions can be anything from the passage of time, receiving a certain amount of cryptocurrency, or the completion of a specific task.
- Execution: When the conditions are satisfied, the contract automatically executes the agreed-upon actions. For example, it might transfer funds from one party to another, register a property transfer, or issue a digital certificate.
- Immutable and Transparent Record: The entire process, including the terms, conditions, and execution, is recorded on the blockchain. This record is immutable (cannot be changed) and transparent, providing an indisputable history of the agreement.
Real-World Examples of Smart Contract Applications
- Finance and Banking: In the financial sector, smart contracts can automate complex financial transactions such as derivatives, bonds, and insurance claims. For instance, AXA, a global insurance company, launched a flight delay insurance product using Ethereum smart contracts. The contract automatically triggers payouts to customers if their flights are delayed beyond a certain threshold.
- Real Estate: Smart contracts streamline real estate transactions by automating processes like property transfers and rental agreements. Propy, a real estate platform, uses blockchain technology to enable property sales through smart contracts, reducing the need for intermediaries and expediting the transaction process.
- Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts enhance transparency and efficiency in supply chains. By tracking goods from production to delivery, they ensure that all parties have access to the same data, reducing fraud and errors. For example, IBM’s Food Trust blockchain network uses smart contracts to trace food products from farm to table, improving food safety and accountability.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, smart contracts can manage patient consent and data sharing. They ensure that patient records are only accessible to authorized parties and can automate insurance claims processing. For example, the company MediBloc is developing a blockchain-based system to securely manage and share health information using smart contracts.
- Legal Industry: The legal industry can benefit from smart contracts by automating routine legal processes, such as contract execution and compliance checks. This reduces the workload for lawyers and ensures that agreements are enforced without the need for manual intervention.
- Gaming and Digital Goods: In the gaming industry, smart contracts enable the creation and transfer of digital assets like in-game items and collectibles. Platforms like Enjin and Decentraland use smart contracts to manage the ownership and trade of virtual goods, providing a secure and transparent marketplace for gamers.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are revolutionizing the way agreements are made and executed by providing a secure, transparent, and efficient alternative to traditional contracts. Their applications span across various industries, from finance and real estate to supply chain management and healthcare, showcasing their versatility and potential to streamline processes and reduce costs. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, smart contracts are poised to become an integral part of our digital future, transforming the way we conduct transactions and build trust in the digital world.