How to Easily Compare Graphics Card Specifications
We talk a lot about the graphic card on this website because most of the time it is the most exciting part of gaming pc and the biggest contributor to your rig gaming performance but that means we’re talking a lot of technical terms like Core clock, GDDR5, CAUD cores, ROPs and so on. If you know all these things mean it is good for you but if you don’t this article is for you. This article helps you to understand GPUs basic and what they mean you should be actually paying attention to those when buying a new GPU.
In fact, let’s start by saying that the terms graphics card, video card, and GPU are all used to refer to one of them.

What is a graphic?
First of all, let’s talk about what is a graphic. A graphic is something that appears on our display. Whether it is a computer display, laptop display, or mobile display.
Example:
Windows 10 start-up menu is graphic,
Android Orio’s new UI Animation is graphic,
And your hand drawing is also graphic
To understand, we take the drawing-
When we draw something, for that we need some tools like a pen, pencil, paper, eraser, and colors. Through this, we do some drawing. Some do design, be it home design, car design, building design, or face design. We call this whole design graphic.

When we design this design on the computer through computer software then we call it computer graphics.

As you must be aware that we use processors to process logical information on computers. Similarly, if we do it to process graphical information, we do it on the graphic card / GPU(Graphical Process Unit).
Earlier we didn’t need graphics cards so much. That we did not have SMART phones and there are not enough good games available in the market. Everyone plays Mario. The most important thing is our operating system, earlier the user interface of our OS was not graphic. We used to access the OS only from the console.
Nowadays our operating system has become very advanced. lots of big software and games are available in the market to run those games and software we need a good graphics card/GPU.
Comparing GPU’s
GPU (Graphics processing unit) actually only means the physical chip that is located on the card’s PCB. Mostly different graphics cards can be made with the same GPU for refrence two biggest desktop GPU manufacturers AMD and Nvidia graphic cards like Radeon RX480 or GeForce GTX1080.

Then vendors like MSI, Asus, Gigabyte and so on often sell that reference design but they also design custom versions with unique coolers io parts, and sometimes a higher clock speed but all these unique versions actually have the same chip at the core so they’re not really that unique.
It’s also possible to have two GPUs on one graphics card like AMDs RG295x2 Radeon pro duo or Nvidias Titan Z those can get tremendous amounts of graphic horsepower but since you’re technically running two GPUs card performance will depend on games how well those games’ support multi-GPU performance Nvidia for their multi-GPU connection is SLI and AMD is crossfire.

sometimes like in the case of Nvidia 70 and 80 cards like the gtx970,980,1070 and 1080 two graphic cards at different tiers will have the same chipple albeit with some modifications the GTX 970 and 980 are both based on Maxwell GM204 GPU while the 1070 and 1080 based on the Pascal GP104.
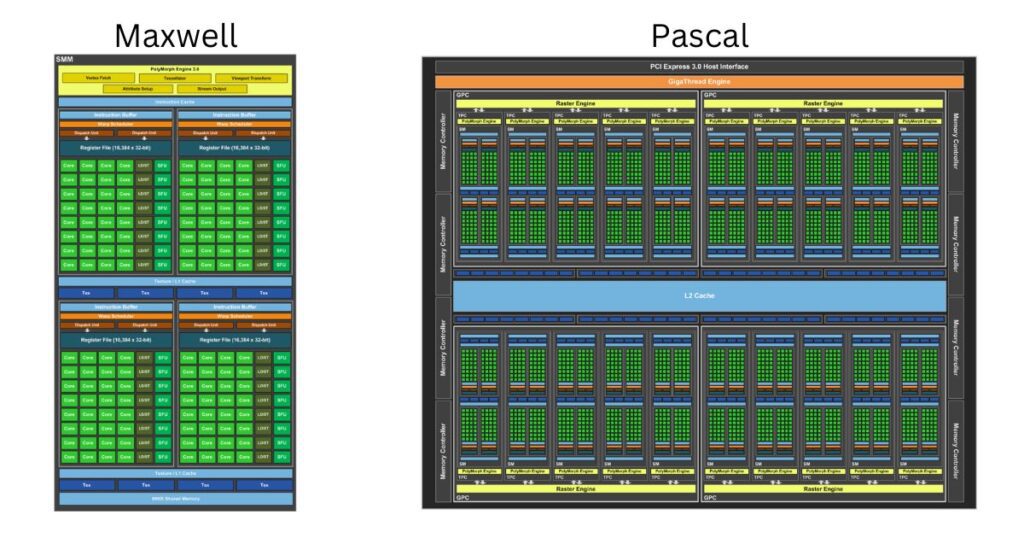
The terms Maxwell and Pascal are related to the GPU architecture. But what does it mean?
What is GPU architecture?
AMD and Nvidia develop the GPUs architecture around every one to two years they often shrink the size of the physical components of the processor, which makes space for more transistors onto the GPU die. The chip architecture changes reduce the amount of power required to run cards. For this reason, it is hard to compare different generations of graphics cards based on certain specifications alone as separate architecture uses the resources available to them differently. Take a look at the first one.
Video Memory/ Video RAM
Video Memory or video RAM serves the same purpose as system RAM in that it holds whatever data is currently being accessed by the GPU these are the textures and images that make up what is displayed to you on your screen. VRAM is essential at higher resolutions.
Having more VRAM won’t automatically get you more frames per second but having not enough could cause textures in games to pop in and out.
4GB of VRAM might be enough for around 1080p with 2GB being found on cheaper cards that would run with some settings turned down and 6 and 8 GB allowing the headroom that’s needed for 1440p and 4k. That’s assuming the card has the raw power necessary to run those resolutions beforehand and games will differ from each other in requirements as well some games are super needy and some will take whatever. One of the indicators of the row power I mentioned earlier is the core clock.
Core clock
Core clock refers to the frequency at which the GPU is running measured in Hz this can be used as a general measure. To compare the power of different GPUs in one generation it can’t reliably be used for comparison between different generations as developments in architecture as we discussed earlier render those comparisons most graphic cards will often have a boost clock.
Boost clock
The boost clock is the maximum safer amount of speed the card can boost itself to for processing heavy loads like a video game. But the performance drops once the graphic card heats up, it’s called thermal throttling and it’s also why you want a good cooler GPU. Similarly, the video Memory runs at the memory clock this is one of a few specs that help us determine the memory bandwidth the other is memory bus width which is how many bits can travel to and from the VRAM each clock cycle GPU either GDDR5, GDDR5X, or HBM which is vertically stacked ram that we’re only seen in AMD FISI and Nvidia Tesla P100 so far.
Memory bandwidth is measured in gigabytes per second think of it as a pipe connecting the GPU to its VRAM the bigger that pipe is more effectively your GPU can use its VRAM having tons and tons of memory won’t be any good if the bandwidth is too small to be used all of it at once.
CUDA cores
CUDA stands for computer unified Device Architecture it’s Nvidia custom programming language CUDA cores are the physical cores in all Nvidia GPUs.
In AMD GPUs these cores call Stream Processors and use they use OpenCL programming language. We don’t compare these cross-generations of architecture for the same reason we don’t do it for core clocks.
Transistor count
Transistor count is the number of transistors in the GPU and it’s too complicated just higher the number, the better.
These next specs are quite complicated and ignorable if you don’t want to be too involved in core knowledge.
Texture units
Texture units assist in applying textures to 3D models.
ROPs
ROPs or Raster Output pipelines or Render Operations units are involved in the final process of outputting pixels to display or rendering. They also deal heavily with anti-aliasing.
TDP
TDP stands for Thermal Design Power. And it’s the maximum amount of heat the GPU is specified to produce when running normal applications.
While looking at specs an even better way for buying a graphic card is better look at its benchmarks and comparing them to other graphic cards in the same price range.